Soft tissue injuries are one of the most common types of injuries that individuals encounter. Whether from sports, accidents, or even everyday activities, these injuries can cause significant discomfort and affect mobility. Injuries typically involve damage to the muscles, tendons, ligaments, and other connective tissues in the body. Understanding injuries is essential for proper treatment, recovery, and prevention. In this blog post, we will explore what soft tissue injuries are, their types, symptoms, causes, treatment options, and how to prevent them. By the end of this guide.
What Are Soft Tissue Injuries?
It refers to damage that occurs to the body’s connective tissues, which include muscles, tendons, ligaments, and fascia. These tissues are responsible for providing structure and support to the body and are involved in nearly every movement we make.
These injuries can occur due to sudden trauma, repetitive stress, or overstretching. injuries are often classified into two categories: acute and chronic. Acute injuries happen suddenly, such as in the case of an accident or sports injury. Chronic injuries develop over time due to repetitive motion or prolonged stress on the tissues.
When a soft tissue injury occurs, it can cause pain, swelling, bruising, and limited movement, depending on the severity of the injury. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential to ensure proper healing and avoid long-term complications.
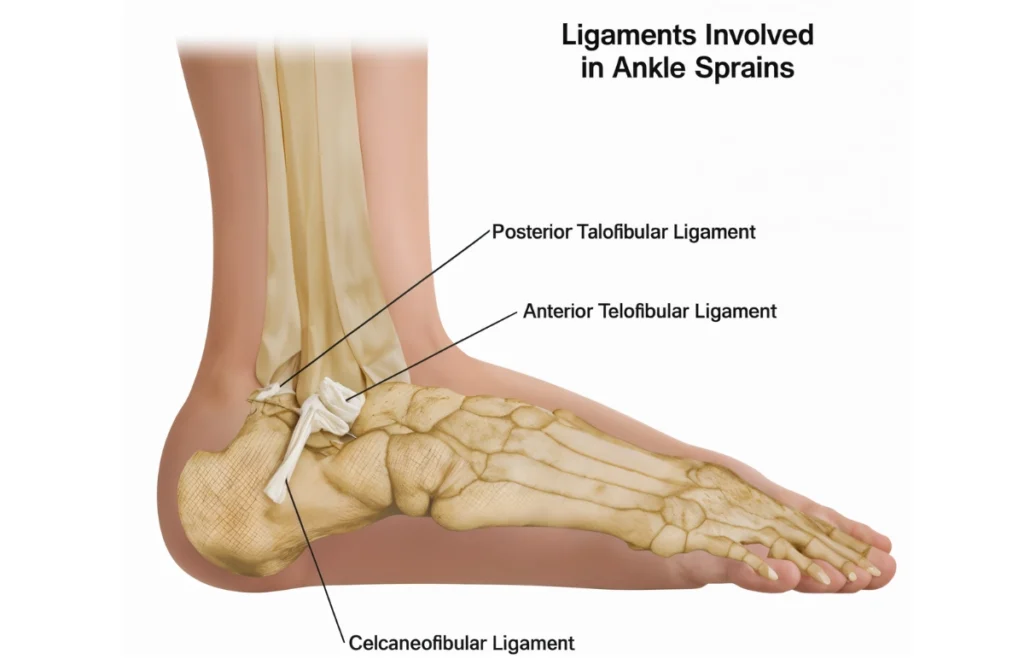
Types of Soft Tissue Injuries
- Sprains: A sprain occurs when a ligament (the tissue that connects bones to other bones) is stretched or torn. Sprains most frequently occur in the ankle, knee, or wrist. They are typically caused by a sudden twisting or impact that forces the joint beyond its normal range of motion. Symptoms of sprains include swelling, bruising, pain, and difficulty moving the affected joint.
- Strains: A strain is an injury to a muscle or tendon (the tissue that connects muscles to bones). Strains often happen due to overstretching or overuse, especially in athletes or individuals who perform repetitive tasks. The symptoms of strains include pain, muscle spasms, swelling, and limited mobility.
- Contusions (Bruises): A contusion is a bruise that occurs when blood vessels under the skin are damaged due to a direct impact. This can cause swelling and discoloration in the affected area. Contusions are common in sports or accidents where the body sustains blunt force trauma.
- Tendonitis: Tendonitis is the inflammation of a tendon, usually due to repetitive motion or overuse. It is common in athletes or people who engage in repetitive activities like typing, painting, or lifting. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and limited movement of the affected area.
Knee Soft Tissue Injury
One of the most common areas where soft tissue injuries occur is the knee. Knee soft tissue injury are often caused by sports, accidents, or even overuse. The knee joint is made up of several soft tissues, including ligaments, tendons, and cartilage, all of which are susceptible to injury.
Some common knee soft tissue injuries include:
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injury: The ACL is one of the key ligaments in the knee that helps stabilize the joint. ACL injuries typically occur in sports that involve sudden changes in direction, such as basketball or soccer. These injuries often require surgical intervention to repair.
- Meniscus Tear: The meniscus is a piece of cartilage in the knee that acts as a cushion between the thigh bone and shin bone. A tear in the meniscus can cause pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the knee.
- Patellar Tendonitis: This condition involves inflammation of the tendon that connects the kneecap to the shin bone. It is common in athletes who perform repetitive jumping movements, such as basketball players.
Soft Tissue Knee Injury Treatment
Treatment for knee soft tissue injuries depends on the severity of the injury and may involve a combination of conservative management, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgical intervention. Below are some common treatments:
- Rest and Ice: Resting the knee and applying ice packs for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce pain and swelling, especially during the initial stages of the injury.
- Compression and Elevation: Using a compression bandage and elevating the knee can further help in reducing swelling. This should be done with care to avoid restricting blood flow.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. However, these should be used as per a healthcare provider’s recommendation.
- Physical Therapy: Once the pain has reduced, physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve flexibility. This will also aid in restoring normal movement patterns and preventing future injuries.
- Knee Bracing: A knee brace can provide support to the joint and limit further damage to the soft tissues, especially in cases of ligament injuries like ACL tears.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, if inflammation persists, a doctor may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and pain, particularly for conditions like patellar tendonitis or meniscus tears.
- Surgical Intervention: For more severe injuries, such as an ACL tear surgery or a significant meniscus tear, surgery may be necessary. ACL reconstruction or meniscus repair surgery can help restore knee function and stability.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy is an emerging treatment option that involves injecting the patient’s own platelets into the injured area to promote healing. This may be considered for chronic soft tissue injuries.
- Stem Cell Therapy: This treatment is sometimes used to help regenerate damaged tissues, particularly in more complex knee injuries, although its effectiveness is still being studied.
Soft Tissue Damage
Soft tissue damage refers to any injury that causes harm to the muscles, tendons, ligaments, or other connective tissues. This damage can range from mild strains to severe tears, and the extent of the damage will determine the severity of the injury.
How Soft Tissue Damage Occurs:
- Trauma: Sudden impact or blunt force trauma can cause bruising, contusions, or tears in the soft tissues.
- Overuse: Repetitive movements or excessive strain on muscles and tendons can lead to tendonitis or stress injuries.
- Sudden Movements: A sudden twist, fall, or awkward movement can cause sprains or strains in the soft tissues.
When soft tissue damage occurs, the body responds with inflammation, swelling, and pain. In more severe cases, the tissue may tear or rupture, requiring medical intervention and, in some cases, surgery. For injuries involving the knee, specialized soft tissue knee injury treatment may be necessary to address the damage and support recovery.
Symptoms
The symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the injury. However, some common symptoms include:
- Pain: The most frequent symptom, which can vary from mild discomfort to intense pain. It may be constant or occur when moving the injured area.
- Swelling: Swelling occurs when fluid accumulates in the injured area due to inflammation. This can make the injured area appear puffy or bloated.
- Bruising: Contusions or bruising often appear when blood vessels are damaged under the skin.
- Limited Mobility: Depending on the injury, movement in the affected area may be restricted, making it difficult to perform normal activities.
Causes
- Accidents: Car accidents, falls, and other sudden events can cause immediate trauma to the soft tissues.
- Sports: Athletes are particularly prone to soft tissue injuries due to the physical demands of sports. Running, jumping, and sudden movements can all contribute to sprains, strains, and other injuries.
- Overuse: Repeating the same motion over an extended period can put excessive strain on the muscles and tendons, leading to tendonitis or stress fractures.
- Improper Technique: Poor posture or improper technique during physical activities can increase the risk of injury.
- Age and Wear: As we age, our tissues become less flexible and more prone to injury.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional. The doctor will assess the injured area for signs of swelling, bruising, and limited movement. They may also ask questions about how the injury occurred and the severity of the symptoms.
In certain situations, rehabilitation through physical therapy is needed to restore strength and movement. These tests can provide a clear picture of the soft tissues and help identify any tears, strains, or inflammation.
Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent further damage and ensure that the injury is treated appropriately.
Treatment
- Rest: Resting the injured area is essential to allow the tissues to heal properly. Avoiding physical activity that could aggravate the injury is important during the initial recovery phase.
- Ice: Placing ice on the injured area can help alleviate pain and decrease swelling. Use ice on the affected area for 15–20 minutes at a stretch, several times a day.
- Compression: Wrapping the injured area with an elastic bandage can help control swelling and provide support.
- Elevation: Raising the injured area above heart level can aid in minimizing swelling.
- Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, can help manage pain and inflammation.
In some cases, physical therapy may be necessary to restore strength and mobility. Severe injuries, such as torn ligaments or tendons, may require surgery to repair the damage. Soft tissue knee injury treatment is a key component of rehabilitation for knee injuries, focusing on restoring knee function and strength through targeted exercises and therapies.
Prevention
Preventing injuries involves taking steps to protect the body and maintain flexibility and strength. Some prevention tips include:
- Warm-up: Always warm up before engaging in physical activity. Stretching and light exercises can prepare the muscles and tendons for more strenuous activity.
- Strengthening Exercises: Building muscle strength can help support the soft tissues and prevent injury.
- Proper Technique: Using the correct form and posture during physical activities can reduce the risk of injury.
- Protective Gear: Wearing appropriate protective gear, such as knee pads or ankle supports, can help prevent injuries in high-risk activities.
- Rest: Avoid overworking your body and allow adequate rest between intense physical activities.
What is a Sprain?
A sprain occurs when a ligament is stretched or torn, leading to pain, swelling, and restricted movement. It is one of the most common soft tissue injuries, particularly in the ankle, knee, and wrist.
Symptoms of a Sprain
- Pain around the affected joint
- Swelling and bruising
- Limited range of motion
- Instability in severe cases
Conclusion
Soft tissue injuries are common but can be effectively managed with the right knowledge and care. Whether it’s a sprain, strain, or more severe soft tissue damage, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for a successful recovery. Prevention plays a significant role in reducing the risk of injury, so be sure to take the necessary precautions to protect your body.
Understanding the nature of injuries, their symptoms, causes, and treatment options empowers you to take control of your health. Remember, injuries are treatable, and with the right approach, you can return to your normal activities with confidence. If you experience any signs of a soft tissue injury, seek medical advice promptly to ensure the best possible outcome.
Read also Limb Lengthening Surgery in Chennai.




